Metadata Report for BODC Series Reference Number 1141016
Metadata Summary
Problem Reports
Data Access Policy
Narrative Documents
Project Information
Data Activity or Cruise Information
Fixed Station Information
BODC Quality Flags
SeaDataNet Quality Flags
Metadata Summary
Data Description |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Data Identifiers |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Time Co-ordinates(UT) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Spatial Co-ordinates | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Parameters |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Problem Reports
No Problem Report Found in the Database
Data Access Policy
Open Data
These data have no specific confidentiality restrictions for users. However, users must acknowledge data sources as it is not ethical to publish data without proper attribution. Any publication or other output resulting from usage of the data should include an acknowledgment.
If the Information Provider does not provide a specific attribution statement, or if you are using Information from several Information Providers and multiple attributions are not practical in your product or application, you may consider using the following:
"Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v1.0."
Narrative Documents
Sea-Bird Dissolved Oxygen Sensor SBE 43 and SBE 43F
The SBE 43 is a dissolved oxygen sensor designed for marine applications. It incorporates a high-performance Clark polarographic membrane with a pump that continuously plumbs water through it, preventing algal growth and the development of anoxic conditions when the sensor is taking measurements.
Two configurations are available: SBE 43 produces a voltage output and can be incorporated with any Sea-Bird CTD that accepts input from a 0-5 volt auxiliary sensor, while the SBE 43F produces a frequency output and can be integrated with an SBE 52-MP (Moored Profiler CTD) or used for OEM applications. The specifications below are common to both.
Specifications
| Housing | Plastic or titanium |
| Membrane | 0.5 mil- fast response, typical for profile applications 1 mil- slower response, typical for moored applications |
| Depth rating | 600 m (plastic) or 7000 m (titanium) 10500 m titanium housing available on request |
| Measurement range | 120% of surface saturation |
| Initial accuracy | 2% of saturation |
| Typical stability | 0.5% per 1000 h |
Further details can be found in the manufacturer's specification sheet.
Sea-Bird Electronics SBE 911 and SBE 917 series CTD profilers
The SBE 911 and SBE 917 series of conductivity-temperature-depth (CTD) units are used to collect hydrographic profiles, including temperature, conductivity and pressure as standard. Each profiler consists of an underwater unit and deck unit or SEARAM. Auxiliary sensors, such as fluorometers, dissolved oxygen sensors and transmissometers, and carousel water samplers are commonly added to the underwater unit.
Underwater unit
The CTD underwater unit (SBE 9 or SBE 9 plus) comprises a protective cage (usually with a carousel water sampler), including a main pressure housing containing power supplies, acquisition electronics, telemetry circuitry, and a suite of modular sensors. The original SBE 9 incorporated Sea-Bird's standard modular SBE 3 temperature sensor and SBE 4 conductivity sensor, and a Paroscientific Digiquartz pressure sensor. The conductivity cell was connected to a pump-fed plastic tubing circuit that could include auxiliary sensors. Each SBE 9 unit was custom built to individual specification. The SBE 9 was replaced in 1997 by an off-the-shelf version, termed the SBE 9 plus, that incorporated the SBE 3 plus (or SBE 3P) temperature sensor, SBE 4C conductivity sensor and a Paroscientific Digiquartz pressure sensor. Sensors could be connected to a pump-fed plastic tubing circuit or stand-alone.
Temperature, conductivity and pressure sensors
The conductivity, temperature, and pressure sensors supplied with Sea-Bird CTD systems have outputs in the form of variable frequencies, which are measured using high-speed parallel counters. The resulting count totals are converted to numeric representations of the original frequencies, which bear a direct relationship to temperature, conductivity or pressure. Sampling frequencies for these sensors are typically set at 24 Hz.
The temperature sensing element is a glass-coated thermistor bead, pressure-protected inside a stainless steel tube, while the conductivity sensing element is a cylindrical, flow-through, borosilicate glass cell with three internal platinum electrodes. Thermistor resistance or conductivity cell resistance, respectively, is the controlling element in an optimized Wien Bridge oscillator circuit, which produces a frequency output that can be converted to a temperature or conductivity reading. These sensors are available with depth ratings of 6800 m (aluminium housing) or 10500 m (titanium housing). The Paroscientific Digiquartz pressure sensor comprises a quartz crystal resonator that responds to pressure-induced stress, and temperature is measured for thermal compensation of the calculated pressure.
Additional sensors
Optional sensors for dissolved oxygen, pH, light transmission, fluorescence and others do not require the very high levels of resolution needed in the primary CTD channels, nor do these sensors generally offer variable frequency outputs. Accordingly, signals from the auxiliary sensors are acquired using a conventional voltage-input multiplexed A/D converter (optional). Some Sea-Bird CTDs use a strain gauge pressure sensor (Senso-Metrics) in which case their pressure output data is in the same form as that from the auxiliary sensors as described above.
Deck unit or SEARAM
Each underwater unit is connected to a power supply and data logging system: the SBE 11 (or SBE 11 plus) deck unit allows real-time interfacing between the deck and the underwater unit via a conductive wire, while the submersible SBE 17 (or SBE 17 plus) SEARAM plugs directly into the underwater unit and data are downloaded on recovery of the CTD. The combination of SBE 9 and SBE 17 or SBE 11 are termed SBE 917 or SBE 911, respectively, while the combinations of SBE 9 plus and SBE 17 plus or SBE 11 plus are termed SBE 917 plus or SBE 911 plus.
Specifications
Specifications for the SBE 9 plus underwater unit are listed below:
| Parameter | Range | Initial accuracy | Resolution at 24 Hz | Response time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | -5 to 35°C | 0.001°C | 0.0002°C | 0.065 sec |
| Conductivity | 0 to 7 S m-1 | 0.0003 S m-1 | 0.00004 S m-1 | 0.065 sec (pumped) |
| Pressure | 0 to full scale (1400, 2000, 4200, 6800 or 10500 m) | 0.015% of full scale | 0.001% of full scale | 0.015 sec |
Further details can be found in the manufacturer's specification sheet.
Turner Designs Self-Contained Underwater Fluorescence Apparatus (SCUFA)
The Turner Designs SCUFA is a submersible fluorometer for chlorophyll and dye tracing operations that has been designed to operate in a wide range of concentrations, environmental conditions as well as operational modes (profiling or moored deployments). The instrument includes an integrated temperature probe and software which allow for automatic correction of fluorescence data from temperature effects. The superior ambient light rejection eliminates the effects of sunlight and allows the SCUFA to be used in surface waters without the need for external pumps or light shields.
Each instrument can be customised to meet user requirements. Users can choose one of the following channels: chlorophyll a, cyanobacteria (phycocyanin or phycoerythrin pigments), rhodamine WT, fluorescein and turbidity. Instrument options include turbidity, internal data logging and automatic temperature correction.
Three versions of the SCUFA are available: SCUFA I, II and III. SCUFA I and II are used for chlorophyll a applications, while SCUFA III is used for Rhodamine WT. Models II and III include a turbidity channel that is not present on model I. The SCUFA has been out of production since 2008.
Specifications
| Depth rating | 600 m |
| Detector | Photodiode |
| Temperature range | -2 to 40°C |
| Maximum sampling rate | 1Hz- digital 5 Hz- analog |
| Resolution | 12 bit- digital 1.2 mV- analog |
| Dynamic Range | |
| Fluorescence | 4 orders of magnitude |
| Turbidity | 3 orders of magnitude |
The table below presents the specifications for the different channels.
| Specifications | Chlorophyll | Cyanobacteria | Rhodamine WT/Fluorescein |
| Light source | Blue | Orange- PC Blue- PE | Green |
| Excitation/Emission | 460/685 | 595/670 (phycocyanin, PC) 528/573 (phycoerythrin, PE) | 530/600 (rhodamine) 490/580 (fluorescein) |
| Minimum detection Limit | |||
| Fluorescence | 0.02 µg L-1 | 150 cells mL-1 | 0.04 ppb |
| Turbidity | 0.05 NTU | 0.05 NTU | 0.05 NTU |
Further details can be found in the manufacturer's brochure.
LI-COR LI-192 Underwater Quantum Sensor
The LI-192 Underwater Quantum Sensor is used to measure photosynthetic photon flux density and is cosine corrected. The sensor is often referred to as LI-192SA or LI-192SB (the LI-192SB model was superseded by LI-192SA). One of the main differences is that the LI-192SA model includes a built-in voltage output for interfacing with NexSens iSIC and SDL data loggers.
Sensor specifications, current at January 2012, are given in the table below. More information can be found in the manufacturer's LI-192SA andLI-192SB specification sheets.
Sensor Specifications
(Specifications apply to both models unless otherwise stated)
| Absolute Calibration | ± 5 % in air traceable to NBS. |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Typically 3 µA per 1000 µmol s-1 m-2 for LI-192SB and 4 µA per 1000 µmol s-1 m-2 for LI-192SA in water. |
| Linearity | Maximum deviation of 1 % up to 10,000 µmol s-1 m-2. |
| Stability | < ± 2 % change over a 1 year period. |
| Response Time | 10 µs. |
| Temperature Dependence | ± 0.15 % per °C maximum. |
| Cosine Correction | Optimized for both underwater and atmospheric use. |
| Azimuth | < ± 1 % error over 360 ° at 45 ° elevation. |
| Detector | High stability silicon photovoltaic detector (blue enhanced). |
| Sensor Housing | Corrosion resistant metal with acrylic diffuser for both saltwater and freshwater applications. Waterproof to withstand 800 psi (5500 kPa) (560 meters). |
SeaTech Transmissometer
Introduction
The transmissometer is designed to accurately measure the the amount of light transmitted by a modulated Light Emitting Diode (LED) through a fixed-length in-situ water column to a synchronous detector.
Specifications
- Water path length: 5 cm (for use in turbid waters) to 1 m (for use in clear ocean waters).
- Beam diameter: 15 mm
- Transmitted beam collimation: <3 milliradians
- Receiver acceptance angle (in water): <18 milliradians
- Light source wavelength: usually (but not exclusively) 660 nm (red light)
Notes
The instrument can be interfaced to Aanderaa RCM7 current meters. This is achieved by fitting the transmissometer in a slot cut into a customized RCM4-type vane.
A red LED (660 nm) is used for general applications looking at water column sediment load. However, green or blue LEDs can be fitted for specilised optics applications. The light source used is identified by the BODC parameter code.
Further details can be found in the manufacturer's Manual.
Prince Madog Cruise PD49_10 CTD Instrumentation
Instrument Descriptions
-
CTD Unit and Auxiliary Sensors
The CTD unit was a Sea-Bird Electronics 911plus system (SN 09P23655-0620), with dissolved oxygen sensor. The CTD was fitted with a red (660 nm) beam transmissometer, a fluorometer, and a LI-COR Underwater Quantum Sensor. Also attached was a Sea-Bird SBE 35 Temperature Logger to supply an independent check of temperature. All instruments were attached to a Sea-Bird SBE 32 compact carousel. The table below lists more detailed information about the various sensors.
Sensor Model Serial Number Calibration (UT) Comments Pressure transducer Paroscientific Digiquartz 42K-105 76076 2004-01-21 - Conductivity sensor SBE 4 2543 2004-01-14 - Temperature sensor SBE 3 P4100 2004-01-21 - Dissolved oxygen SBE 43 1491 2008-08-15 - Transmissometer (660 nm) SeaTech T1000 T1021 1998-03-03 0.2 m path Fluorometer Turner SCUFA II 262 - - LI-COR (contains CEFAS in-house electronics) LI-192SB CEFAS #69 2009-04-17 - Temperature Logger SBE 35 0041 2005-03-29 - Change of sensors during cruise: None reported.
-
Sampling device
Rosette sampling system equipped with 5 l sampling bottles (Sea-Bird Improved PVC Sample Bottles based on design of Ocean Test Equipment Inc. model 110 bottle).
Prince Madog Cruise PD49_10 CTD Processing
Originator's Data Processing
-
Sampling Strategy
A total of 11 CTD profiles were performed during the cruise throughout Liverpool Bay. Data were measured at 24 Hz and logged to a PC running SEASAVE, Sea-Bird's data acquisition software. Rosette bottles were fired throughout the water column on the upcast of the CTD profiles. Independent temperature data were recorded at the time of each bottle firing.
Salinity samples were taken from near-bed bottles, then returned to Bangor University (BU), where salinity was determined using a Portasal salinometer that was calibrated to standard seawater. The raw Sea-Bird data, configuration and bottle files were supplied to BODC for further processing.
BODC Processing
-
Data Processing
The raw CTD files were processed through the Sea-Bird SBE Data Processing software version 7.20e. Binary (.HEX) files were converted to engineering units and ASCII format (.CNV) using the DATCNV program.
Sea-Bird bottle files (.BTL), with information on pressure and other logged readings at the time of bottle firing, were also generated during the data conversion process.
WILDEDIT was not run on the data as no pressure spikes were present in the casts. FILTER was run on the pressure channel using the recommended time filter of 0.15 s.
Sea-Bird software program ALIGN CTD was run to advance conductivity by 0 s and oxygen by 2 s (within the typical range given in the Sea-Bird manual). No adjustment was made to the temperature channel as the fast sensor response time renders this unnecessary, according to the Sea-Bird literature.
To compensate for conductivity cell thermal mass effects, the data files were run through CELLTM, using alpha = 0.03, 1/beta = 7, typical values for this CTD model given in the Sea-Bird literature. LOOP EDIT was run to identify scans which were affected by ship heave. Salinity, density (Sigma-theta kg m-3) and oxygen concentration (ml l-1) were then calculated and added to the output files using the DERIVE program. BINAVERAGE was used to bin the data (both upcasts and downcasts) to 10 Hz and remove cycles flagged by LOOP EDIT. Finally, the first oxygen concentration channel and first salinity channel (both generated by DATCNV using data un-adjusted by ALIGN CTD and CELLTM) were dropped using STRIP.
-
Reformatting
The data were converted from ASCII format into BODC internal format using a transfer function. The following table shows how the variables within the ASCII files were mapped to appropriate BODC parameter codes:
Originator's Parameter Name Units Description BODC Parameter Code Units Comments Pressure, Digiquartz dbar Pressure of water body on profiling pressure sensor PRESPR01 dbar - Conductivity S m-1 Electrical conductivity of the water column by CTD CNDCST01 S m-1 - Oxygen raw, SBE 43 Volts Instrument output (voltage) from SBE 43 sensor OXYVTLN1 Volts Intermediate voltage channel has not been included in the final dataset. Oxygen, SBE 43 ml l-1 Dissolved oxygen concentration from SBE 43 sensor DOXYSU01 µmol l-1 Converted from ml l-1 to µmol l-1 by multiplying the original value by 44.66. Salinity, Practical PSU Practical salinity of the water body by CTD PSALCU01 - Generated by Sea-Bird software from CTD temperature and conductivity data. No calibrated data available for this channel. Temperature [ITS-90] °C Temperature of water column by CTD TEMPCU01 °C Uncalibrated channel has not been included in the final dataset. Voltage 2 Un-adjusted volts Voltage from CTD PAR Sensor LVLTLD01 Un-adjusted volts Intermediate voltage channel has not been included in the final dataset. Voltage 3 Un-adjusted volts Beam transmissometer voltage TVLTCR01 Un-adjusted volts Intermediate voltage channel has not been included in the final dataset. Voltage 4 Un-adjusted volts Voltage from CTD SCUFA II Turner fluorometer FVLTWS01 Un-adjusted volts - - - Potential temperature POTMCV01 °C Generated by BODC using UNESCO Report 38 (1981) algorithm with parameters PSALCU01 and TEMPCC01 - - Sigma-theta SIGTPR01 kg m-3 Generated by BODC using the Fofonoff and Millard (1983) algorithm - - PAR IRRDUV01 µE m-2 s-1 Generated by BODC from calibration of LVLTLD01 - - Beam Attenuation ATTNMR01 m-1 Generated by BODC from calibration of TVLTCR01 - - Temperature TEMPCC01 °C Generated by BODC from calibration of TEMPCU01 - - Oxygen saturation OXYSSU01 % Generated by BODC during transfer using the Benson and Krause (1984) algorithm. -
Screening
Reformatted CTD data were visualised using the in-house graphical editor EDSERPLO. Downcasts and upcasts were differentiated and the limits manually flagged. No data values were edited or deleted. Flagging was achieved by modification of the associated quality control flag to 'M' for suspect values and 'N' for nulls.
-
Banking
Once quality control screening was complete, CTD downcasts for casts 003-004 and 007-008 and upcasts for casts 002, 005-006 and 009-011 were loaded into BODC's shelf sea database under the Oracle Relational Database Management System. Data from cast 001 have not been loaded to the dataset. For casts 002, 005-006 and 009-011 the upcast was used as the oxygen sensor appeared to have not reached equilibrium on the downcast. Data from cast 001 were considered suspect during screening. Subsequent correspondence with the data originator identified that there were significant pump failures during this cast. As a result these data have not been banked. The raw data are available on request but should only be used with caution.
These data have since (2013) been extracted from the relational database and transferred into BODC internal format for distribution as series (complete profiles).
-
References
Benson, BB and Krause, D (1984). The concentration and isotopic fractionation of oxygen dissolved in freshwater and seawater in equilibrium with the atmosphere. Limnol. Oceanogr., 29(3), 620-632
Fofonoff, NP and Millard, RC (1983). Algorithms for computations of fundamental properties of seawater. UNESCO Technical Papers in Marine Science No. 44, 53pp.
UNESCO, 1981. Background papers and supporting data on the International Equation of State of Seawater 1980. UNESCO Technical Papers in Marine Science No. 38, 192pp
Field Calibrations
-
Salinity
It was not possible to calibrate the CTD salinity against field samples. Only nine independent salinity values (obtained from water samples from the CTD rosette) were collected and this population size is too small to allow valid statistical analysis. Therefore, the only calibration applied to the CTD salinity has been the manufacturer calibration, carried out during CTD processing. The mean offset between independent salinity and CTD salinity (Autosal salinity - CTD salinity) was found to be -0.015333 with a standard deviation = 0.002430.
-
Temperature
46 independent temperature values were compared to CTD temperature (data values sampled from cast 001 have been excluded due to data quality problems with the CTD data). Five additional data points were identified as outliers and excluded from the analysis. The temperature offset (SBE 35 temperature - CTD temperature) was found, using regression analysis, not to be statistically related to SBE 35 temperature at a 95% confidence level. The mean offset = - 0.0024621 °C and the standard deviation for this dataset = 0.004149 °C. This is at the lowest level of accuracy for both the SBE 35 and Sea-Bird 911plus CTD (+/- 0.001 °C). Therefore, there was no adjustment to the CTD temperature resulting from the application of manufacturers coefficients during initial processing.
-
Pressure
There were no casts where the CTD pressure was logging in air. No adjustments were made to the values resulting from application of manufacturer's coefficients during the initial processing.
-
Beam attenuation
Coefficients M and B were calculated, allowing calibration of the transmissometer with air readings taken during the cruise. M and B are calculated according to SBE Application Note No. 7:
M = (Tw/W0)*(A0-Y0)/(A1-Y1) B= -M*Y1 Where Tw is the percent transmission for pure water for the instrument (92.98%); W0 is the voltage output in pure water (4.649 volts); A0 is the manufacturer's air voltage (4.661 volts); Y0 is the manufacturer's blocked path voltage (0.000 volts); A1 is the cruise maximum air voltage (4.1978 volts); Y1 is the current blocked path voltage (0.00 volts). For this cruise, M and B were calculated to be 22.2069 and 0, respectively.
M and B are then inserted into the following equations (from SBE Application Note No. 7) to obtain calibrated beam attenuation:
whereLight transmission [%] = (M * voltage output) + B Beam attenuation coefficient c = - (1/z) * ln (light transmission [decimal]) M and B are the calibration coefficients, z is the transmissometer path length (0.2 m), light transmission[decimal] is light transmission [%] divided by 100, c = beam attenuation (m-1)
-
PAR
During instrument deployment, no effort was made to avoid data collection possibly being affected by ship shadowing. The LI-COR LI-192SB sensor number 69 was calibrated from raw voltages using the CEFAS supplied equation:
PAR (µE m-2 s-1) = 0.151282*exp(measured voltage * 3.432)
Project Information
Oceans 2025 - The NERC Marine Centres' Strategic Research Programme 2007-2012
Who funds the programme?
The Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) funds the Oceans 2025 programme, which was originally planned in the context of NERC's 2002-2007 strategy and later realigned to NERC's subsequent strategy (Next Generation Science for Planet Earth; NERC 2007).
Who is involved in the programme?
The Oceans 2025 programme was designed by and is to be implemented through seven leading UK marine centres. The marine centres work together in coordination and are also supported by cooperation and input from government bodies, universities and other partners. The seven marine centres are:
- National Oceanography Centre, Southampton (NOCS)
- Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML)
- Marine Biological Association (MBA)
- Sir Alister Hardy Foundation for Marine Science (SAHFOS)
- Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory (POL)
- Scottish Association for Marine Science (SAMS)
- Sea Mammal Research Unit (SMRU)
Oceans2025 provides funding to three national marine facilities, which provide services to the wider UK marine community, in addition to the Oceans 2025 community. These facilities are:
- British Oceanographic Data Centre (BODC), hosted at POL
- Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level (PSMSL), hosted at POL
- Culture Collection of Algae and Protozoa (CCAP), hosted at SAMS
The NERC-run Strategic Ocean Funding Initiative (SOFI) provides additional support to the programme by funding additional research projects and studentships that closely complement the Oceans 2025 programme, primarily through universities.
What is the programme about?
Oceans 2025 sets out to address some key challenges that face the UK as a result of a changing marine environment. The research funded through the programme sets out to increase understanding of the size, nature and impacts of these changes, with the aim to:
- improve knowledge of how the seas behave, not just now but in the future;
- help assess what that might mean for the Earth system and for society;
- assist in developing sustainable solutions for the management of marine resources for future generations;
- enhance the research capabilities and facilities available for UK marine science.
In order to address these aims there are nine science themes supported by the Oceans 2025 programme:
- Climate, circulation and sea level (Theme 1)
- Marine biogeochemical cycles (Theme 2)
- Shelf and coastal processes (Theme 3)
- Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning (Theme 4)
- Continental margins and deep ocean (Theme 5)
- Sustainable marine resources (Theme 6)
- Technology development (Theme 8)
- Next generation ocean prediction (Theme 9)
- Integration of sustained observations in the marine environment (Theme 10)
In the original programme proposal there was a theme on health and human impacts (Theme 7). The elements of this Theme have subsequently been included in Themes 3 and 9.
When is the programme active?
The programme started in April 2007 with funding for 5 years.
Brief summary of the programme fieldwork/data
Programme fieldwork and data collection are to be achieved through:
- physical, biological and chemical parameters sampling throughout the North and South Atlantic during collaborative research cruises aboard NERC's research vessels RRS Discovery, RRS James Cook and RRS James Clark Ross;
- the Continuous Plankton Recorder being deployed by SAHFOS in the North Atlantic and North Pacific on 'ships of opportunity';
- physical parameters measured and relayed in near real-time by fixed moorings and ARGO floats;
- coastal and shelf sea observatory data (Liverpool Bay Coastal Observatory (LBCO) and Western Channel Observatory (WCO)) using the RV Prince Madog and RV Quest.
The data is to be fed into models for validation and future projections. Greater detail can be found in the Theme documents.
Oceans 2025 Theme 10
Oceans 2025 is a strategic marine science programme, bringing marine researchers together to increase people's knowledge of the marine environment so that they are better able to protect it for future generations.
Theme 10: Integration of Sustained Observations in the Marine Environment spans all marine domains from the sea-shore to the global ocean, providing data and knowledge on a wide range of ecosystem properties and processes (from ocean circulation to biodiversity) that are critical to understanding Earth system behaviour and identifying change. They have been developed not merely to provide long-term data sets, but to capture extreme or episodic events, and play a key role in the initialisation and validation of models. Many of these SOs will be integrated into the newly developing UK Marine Monitoring Strategy - evolving from the Defra reports Safeguarding our Seas (2002) and Charting Progress (2005), thus contributing to the underpinning knowledge for national marine stewardship. They will also contribute to the UK GOOS Strategic Plan (IACMST, 2006) and the Global Marine Assessment.
Weblink: http://www.oceans2025.org/
Oceans 2025 Theme 10, Sustained Observation Activity 11: Liverpool Bay and Irish Sea Coastal Observatory
Sustained, systematic observations of the ocean and continental shelf seas at appropriate time and space scales allied to numerical models are key to understanding and prediction. In shelf seas these observations address issues as fundamental as 'what is the capacity of shelf seas to absorb change?' encompassing the impacts of climate change, biological productivity and diversity, sustainable management, pollution and public health, safety at sea and extreme events. Advancing understanding of coastal processes to use and manage these resources better is challenging; important controlling processes occur over a broad range of spatial and temporal scales which cannot be simultaneously studied solely with satellite or ship-based platforms.
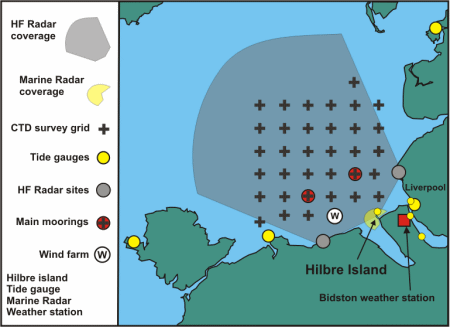
Considerable effort has been spent by the Proudman Oceangraphic Laboratory (POL) in the years 2001 - 2006 in setting up an integrated observational and now-cast modelling system in Liverpool Bay (see Figure), with the recent POL review stating the observatory was seen as a leader in its field and a unique 'selling' point of the laboratory. Cost benefit analysis (IACMST, 2004) shows that benefits really start to accrue after 10 years. In 2007 - 2012 exploitation of (i) the time series being acquired, (ii) the model-data synthesis and (iii) the increasingly available quantities of real-time data (e.g. river flows) can be carried out through Sustained Observation Activity (SO) 11, to provide an integrated assessment and short term forecasts of the coastal ocean state.
Overall Aims and Purpose of SO 11
- To continue and enlarge the scope of the existing coastal observatory in Liverpool Bay to routinely monitor the northern Irish Sea
- To develop the synthesis of measurements and models in the coastal ocean to optimize measurement arrays and forecast products. Driving forward shelf seas' operational oceanography with the direct objective of improving the national forecasting capability, expressed through links to the National Centre for Ocean Forecasting (NCOF)
- To exploit the long time-series of observations and model outputs to: a) identify the roles of climate and anthropogenic inputs on the coastal ocean's physical and biological functioning (including impacts of nutrient discharges, offshore renewable energy installations and fishing activity) taking into consideration the importance of events versus mean storms / waves, river discharge / variable salinity stratification / horizontal gradients; b) predict the impacts of climate change scenarios; and c) provide new insights to Irish Sea dynamics for variables either with seasonal cycles and interannual variability, or which show weak or no seasonal cycles
- To provide and maintain a 'laboratory' within which a variety of observational and model experiments can be undertaken (Oceans 2025 Themes 3, 6, 8, 9), including capture of extreme events
- Demonstrate the value of an integrated approach in assessment and forecasting
- Demonstrate the coastal observatory as a tool for marine management strategies through collaboration with the Environment Agency (EA), Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA), Joint Nature Conservation Commmittee (JNCC), English Nature (EN), Department of Agriculture and Rural Development (DARD), and Local Authorities, providing management information pertinent to policy (e.g. Water Framework Directive)
Measurement and Modelling Activities
- East Mooring Site: Bottom frame with full suite of physical measurements (high frequency Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP), conductivity, temperature, turbidity and fluorescence), a Centre for Environment, Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (CEFAS) directional wavebuoy, and a CEFAS Smartbuoy collecting surface properties including salinity, temperature, turbidity, nutrients, irradiance and chlorophyll. All transmit data in real-time via Orbcomm. The Smartbuoy also collects daily water samples.
- West Mooring Site: Bottom frame with full suite of physical measurements (high frequency ADCP, conductivity, temperature, turbidity and fluorescence), CEFAS Smartbuoy.
- Spatial Survey: Four - six week intervals (determined by biofouling of optical sensors). Spatial surveys comprise of vertical profiles of CTD, suspended particulate material (SPM), some bed sediment sampling and surface and bed nutrients, phytoplankton, zooplankton.
- Ferry: The Birkenhead - Belfast ferry samples near surface (5 m depth) temperature, salinity, turbidity, chlorophyll, with data transmitted by Orbcomm. The route is scientifically varied passing through six completely different hydrodynamic regions, which significantly impact on their ecological function.
- Tide gauges: Real-time data are obtained from tide gauges operated by Mersey Docks and Harbour Company (MDHC) and the UK tide gauge network.
- Satellite imagery: Weekly composite satellite data, Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) sea surface temperature (SST) and ocean colour (chlorophyll and suspended sediment), are provided by the Remote Sensing Data Analysis Service (RSDAS) based at Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML).
- HF radar: A phased array HF radar system (a 12-16MHz WERA HF radar) measuring surface currents and waves with maximum range 75km at a resolution of 4km for sea surface currents and for 2-D wave spectra.
- Meteorology station: With web camera, located on Hilbre Island at the mouth of the Dee Estuary
- Operational models: The Coastal Observatory uses Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory Coastal Ocean Modelling System (POLCOMS), which is part of Oceans 2025 Theme 9.
More detailed information on this Work Package is available at pages 32 - 35 of the official Oceans 2025 Theme 10 document: Oceans 2025 Theme 10
Weblink: http://www.oceans2025.org/
References:
IACMST., 2004. The Economics of Sustained Marine Measurements. IACMST Information Document, N0.11, Southampton: IACMST, 96 pp
Data Activity or Cruise Information
Cruise
| Cruise Name | PD49/10 |
| Departure Date | 2010-12-07 |
| Arrival Date | 2010-12-08 |
| Principal Scientist(s) | John Kenny (National Oceanography Centre, Liverpool) |
| Ship | RV Prince Madog |
Complete Cruise Metadata Report is available here
Fixed Station Information
Fixed Station Information
| Station Name | Coastal Observatory Site 20 |
| Category | Offshore area |
| Latitude | 53° 32.13' N |
| Longitude | 3° 38.39' W |
| Water depth below MSL | 32.5 m |
Liverpool Bay Coastal Observatory Site 20
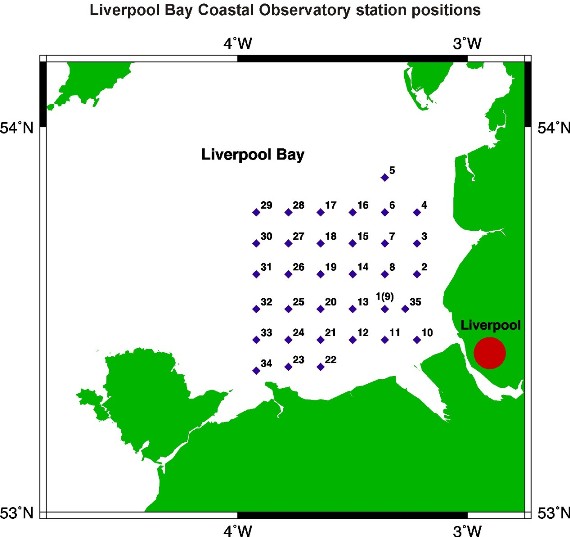
This station is one of 34 stations regularly visited by the Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory (POL) as part of the Liverpool Bay Coastal Observatory. During each site visit CTD profiles are collected and since March 2010 (when this became the secondary mooring site for the Coastal Observatory (also known as Site B)) moorings are deployed. The station lies within a box of mean water depth 32.5 m with the following co-ordinates:
| Box Corner | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| North-west corner | 53.54052° | -3.65075° |
| South-east corner | 53.53041° | -3.62923° |
The position of this station relative to the other POL Coastal Observatory sites can be seen from the figure below.
CTD Sampling History
| Year | Number of Visits | Total Casts per year |
| 2011 | 5 | 11 |
| 2010 | 8 | 22 |
| 2009 | 6 | 6 |
| 2008 | 7 | 7 |
| 2007 | 7 | 7 |
| 2006 | 7 | 8 |
| 2005 | 7 | 7 |
| 2004 | 8 | 8 |
| 2003 | 9 | 9 |
| 2002 | 2 | 2 |
The CTD instrument package for these cruises was a Sea-Bird 911plus, with beam transmissometer, fluorometer, LICOR PAR sensor, LISST-25, and oxygen sensor.
Related Fixed Station activities are detailed in Appendix 1
BODC Quality Control Flags
The following single character qualifying flags may be associated with one or more individual parameters with a data cycle:
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
| Blank | Unqualified |
| < | Below detection limit |
| > | In excess of quoted value |
| A | Taxonomic flag for affinis (aff.) |
| B | Beginning of CTD Down/Up Cast |
| C | Taxonomic flag for confer (cf.) |
| D | Thermometric depth |
| E | End of CTD Down/Up Cast |
| G | Non-taxonomic biological characteristic uncertainty |
| H | Extrapolated value |
| I | Taxonomic flag for single species (sp.) |
| K | Improbable value - unknown quality control source |
| L | Improbable value - originator's quality control |
| M | Improbable value - BODC quality control |
| N | Null value |
| O | Improbable value - user quality control |
| P | Trace/calm |
| Q | Indeterminate |
| R | Replacement value |
| S | Estimated value |
| T | Interpolated value |
| U | Uncalibrated |
| W | Control value |
| X | Excessive difference |
SeaDataNet Quality Control Flags
The following single character qualifying flags may be associated with one or more individual parameters with a data cycle:
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | no quality control |
| 1 | good value |
| 2 | probably good value |
| 3 | probably bad value |
| 4 | bad value |
| 5 | changed value |
| 6 | value below detection |
| 7 | value in excess |
| 8 | interpolated value |
| 9 | missing value |
| A | value phenomenon uncertain |
| B | nominal value |
| Q | value below limit of quantification |
Appendix 1: Coastal Observatory Site 20
Related series for this Fixed Station are presented in the table below. Further information can be found by following the appropriate links.
If you are interested in these series, please be aware we offer a multiple file download service. Should your credentials be insufficient for automatic download, the service also offers a referral to our Enquiries Officer who may be able to negotiate access.
| Series Identifier | Data Category | Start date/time | Start position | Cruise |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1013118 | CTD or STD cast | 2006-11-02 06:18:00 | 53.53267 N, 3.64367 W | RV Prince Madog PD35/06 |
| 979271 | CTD or STD cast | 2007-02-15 17:26:00 | 53.53317 N, 3.63867 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/07 |
| 937772 | CTD or STD cast | 2007-04-20 02:36:00 | 53.53767 N, 3.64383 W | RV Prince Madog PD06/07 |
| 942239 | CTD or STD cast | 2007-05-17 06:12:00 | 53.53283 N, 3.63633 W | RV Prince Madog PD09/07 |
| 942995 | CTD or STD cast | 2007-06-21 06:23:00 | 53.5365 N, 3.64517 W | RV Prince Madog PD13/07 |
| 943396 | CTD or STD cast | 2007-07-27 06:37:00 | 53.53367 N, 3.62917 W | RV Prince Madog PD16/07 |
| 943808 | CTD or STD cast | 2007-08-30 05:46:00 | 53.53267 N, 3.6425 W | RV Prince Madog PD20/07 |
| 945759 | CTD or STD cast | 2007-10-04 06:47:00 | 53.5315 N, 3.63883 W | RV Prince Madog PD23/07 |
| 946818 | CTD or STD cast | 2008-01-11 02:24:00 | 53.53517 N, 3.6435 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/08 |
| 947084 | CTD or STD cast | 2008-03-14 05:52:00 | 53.533 N, 3.64533 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/08 |
| 947397 | CTD or STD cast | 2008-04-17 06:12:00 | 53.53583 N, 3.637 W | RV Prince Madog PD09/08 |
| 948235 | CTD or STD cast | 2008-05-15 13:00:00 | 53.53367 N, 3.64517 W | RV Prince Madog PD14/08 |
| 948585 | CTD or STD cast | 2008-06-25 20:03:00 | 53.53367 N, 3.641 W | RV Prince Madog PD19/08 |
| 949472 | CTD or STD cast | 2008-07-31 07:10:00 | 53.53367 N, 3.6365 W | RV Prince Madog PD23/08 |
| 950079 | CTD or STD cast | 2008-12-11 06:25:00 | 53.53117 N, 3.6365 W | RV Prince Madog PD37/08 |
| 950485 | CTD or STD cast | 2009-02-06 09:50:00 | 53.53367 N, 3.64533 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/09B |
| 951464 | CTD or STD cast | 2009-04-02 03:57:00 | 53.53183 N, 3.64217 W | RV Prince Madog PD12/09 |
| 953803 | CTD or STD cast | 2009-05-13 11:24:00 | 53.53433 N, 3.64083 W | RV Prince Madog PD18/09 |
| 1023149 | CTD or STD cast | 2009-06-17 21:35:00 | 53.53167 N, 3.64483 W | RV Prince Madog PD24/09 |
| 1023487 | CTD or STD cast | 2009-08-03 14:35:00 | 53.53283 N, 3.6415 W | RV Prince Madog PD33/09 |
| 1024349 | CTD or STD cast | 2009-09-16 04:31:00 | 53.53383 N, 3.643 W | RV Prince Madog PD38/09 |
| 1641347 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-01-26 11:40:03 | 53.53783 N, 3.64033 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1624135 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2010-01-26 11:45:00 | 53.53783 N, 3.64033 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1030380 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-01-26 13:08:00 | 53.539 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1641384 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-01-26 13:10:00 | 53.53833 N, 3.64033 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1641396 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-01-26 13:10:00 | 53.53833 N, 3.64033 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1641323 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-01-26 13:10:01 | 53.53833 N, 3.64033 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1641335 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-01-26 13:10:02 | 53.53833 N, 3.64033 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1075687 | Fluorescence or pigments | 2010-01-26 14:00:00 | 53.5383 N, 3.6403 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1075558 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-01-26 14:00:00 | 53.5383 N, 3.6403 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1076629 | Transmittance/attenuance, turbidity, or SPM conc. | 2010-01-26 14:00:00 | 53.5383 N, 3.6403 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1030564 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-01-27 06:05:00 | 53.54083 N, 3.63667 W | RV Prince Madog PD02/10 |
| 1038333 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-03-17 15:37:00 | 53.5395 N, 3.64383 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1641440 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-03-17 16:40:03 | 53.53783 N, 3.64217 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1624080 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2010-03-17 16:45:00 | 53.53783 N, 3.64217 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1641488 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-03-17 16:50:00 | 53.539 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1641507 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-03-17 16:50:00 | 53.539 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1641415 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-03-17 16:50:01 | 53.539 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1641439 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-03-17 16:50:01 | 53.539 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1075699 | Fluorescence or pigments | 2010-03-17 17:00:00 | 53.539 N, 3.6402 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1075571 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-03-17 17:00:00 | 53.539 N, 3.6402 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1076120 | Transmittance/attenuance, turbidity, or SPM conc. | 2010-03-17 17:00:00 | 53.539 N, 3.6402 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1038345 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-03-17 17:03:00 | 53.54 N, 3.6435 W | RV Prince Madog PD05/10 |
| 1641556 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-04-28 17:40:03 | 53.5395 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD10/10 |
| 1624031 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2010-04-28 17:45:00 | 53.5395 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD10/10 |
| 1075706 | Fluorescence or pigments | 2010-04-28 18:00:00 | 53.5408 N, 3.6392 W | RV Prince Madog PD10/10 |
| 1075583 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-04-28 18:00:00 | 53.5408 N, 3.6392 W | RV Prince Madog PD10/10 |
| 1641600 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-04-28 18:00:00 | 53.54083 N, 3.63917 W | RV Prince Madog PD10/10 |
| 1641612 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-04-28 18:00:00 | 53.54083 N, 3.63917 W | RV Prince Madog PD10/10 |
| 1076630 | Transmittance/attenuance, turbidity, or SPM conc. | 2010-04-28 18:00:00 | 53.5408 N, 3.6392 W | RV Prince Madog PD10/10 |
| 1641519 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-04-28 18:00:01 | 53.54083 N, 3.63917 W | RV Prince Madog PD10/10 |
| 1641532 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-04-28 18:00:01 | 53.54083 N, 3.63917 W | RV Prince Madog PD10/10 |
| 1090696 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-06-10 16:48:00 | 53.53833 N, 3.638 W | RV Prince Madog PD17/10 |
| 1641685 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-06-10 18:00:03 | 53.53917 N, 3.641 W | RV Prince Madog PD17/10 |
| 1624079 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2010-06-10 18:05:00 | 53.53917 N, 3.641 W | RV Prince Madog PD17/10 |
| 1075718 | Fluorescence or pigments | 2010-06-10 18:30:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.6386 W | RV Prince Madog PD17/10 |
| 1075595 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-06-10 18:30:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.6386 W | RV Prince Madog PD17/10 |
| 1090703 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-06-10 19:05:00 | 53.54333 N, 3.63433 W | RV Prince Madog PD17/10 |
| 1090893 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-07-07 21:40:00 | 53.543 N, 3.63967 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1090997 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-07-08 06:04:00 | 53.53617 N, 3.635 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1641790 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-07-08 07:40:03 | 53.5395 N, 3.64083 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1624043 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2010-07-08 07:45:00 | 53.5395 N, 3.64083 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1075731 | Fluorescence or pigments | 2010-07-08 08:00:00 | 53.5378 N, 3.6367 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1075602 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-07-08 08:00:00 | 53.5378 N, 3.6367 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1641833 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-07-08 08:10:00 | 53.53783 N, 3.63667 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1641845 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-07-08 08:10:00 | 53.53783 N, 3.63667 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1641741 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-07-08 08:10:01 | 53.53783 N, 3.63667 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1641777 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-07-08 08:10:01 | 53.53783 N, 3.63667 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1091000 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-07-08 08:25:00 | 53.54233 N, 3.63367 W | RV Prince Madog PD21/10 |
| 1112294 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-08-12 06:06:00 | 53.53467 N, 3.64383 W | RV Prince Madog PD29/10 |
| 1112405 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-08-12 18:07:00 | 53.539 N, 3.643 W | RV Prince Madog PD29/10 |
| 1641870 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-08-12 19:10:03 | 53.5395 N, 3.64117 W | RV Prince Madog PD29/10 |
| 1112417 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-08-12 19:11:00 | 53.53667 N, 3.6385 W | RV Prince Madog PD29/10 |
| 1623967 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2010-08-12 19:15:00 | 53.5395 N, 3.64117 W | RV Prince Madog PD29/10 |
| 1114160 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-09-29 04:05:00 | 53.5315 N, 3.64317 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1114196 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-09-29 07:03:00 | 53.541 N, 3.64433 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1641962 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-09-29 07:50:03 | 53.54017 N, 3.64167 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1623851 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2010-09-29 07:55:00 | 53.54017 N, 3.64167 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1075743 | Fluorescence or pigments | 2010-09-29 08:30:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.6363 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1075614 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-09-29 08:30:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.6363 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1641998 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-09-29 08:30:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.63633 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1642001 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-09-29 08:30:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.63633 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1076132 | Transmittance/attenuance, turbidity, or SPM conc. | 2010-09-29 08:30:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.6363 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1641913 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-09-29 08:30:01 | 53.5405 N, 3.63633 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1641937 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-09-29 08:30:01 | 53.5405 N, 3.63633 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1114203 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-09-29 08:51:00 | 53.54033 N, 3.63717 W | RV Prince Madog PD36/10 |
| 1642062 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-12-07 15:20:03 | 53.5405 N, 3.64283 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1623666 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2010-12-07 15:25:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.64283 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1642098 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-12-07 16:10:00 | 53.537 N, 3.638 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1642105 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-12-07 16:10:00 | 53.537 N, 3.638 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1642117 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-12-07 16:10:00 | 53.537 N, 3.638 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1642013 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-12-07 16:10:01 | 53.537 N, 3.638 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1642025 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-12-07 16:10:01 | 53.537 N, 3.638 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1075755 | Fluorescence or pigments | 2010-12-07 16:30:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.6428 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1075626 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2010-12-07 16:30:00 | 53.5405 N, 3.6428 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1140953 | CTD or STD cast | 2010-12-07 16:46:00 | 53.53667 N, 3.646 W | RV Prince Madog PD49/10 |
| 1149067 | CTD or STD cast | 2011-01-13 08:03:00 | 53.54033 N, 3.64283 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1149079 | CTD or STD cast | 2011-01-13 09:10:00 | 53.543 N, 3.6415 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1642178 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-01-13 09:10:03 | 53.54033 N, 3.64383 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1623771 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2011-01-13 09:14:59 | 53.54033 N, 3.64383 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1642209 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-01-13 15:10:00 | 53.54017 N, 3.63983 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1642210 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-01-13 15:10:00 | 53.54017 N, 3.63983 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1642222 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-01-13 15:10:00 | 53.54017 N, 3.63983 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1642130 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-01-13 15:10:01 | 53.54017 N, 3.63983 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1642142 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-01-13 15:10:01 | 53.54017 N, 3.63983 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1149159 | CTD or STD cast | 2011-01-13 15:32:00 | 53.53833 N, 3.637 W | RV Prince Madog PD01/11 |
| 1149946 | CTD or STD cast | 2011-03-17 08:59:00 | 53.53833 N, 3.63967 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1150112 | CTD or STD cast | 2011-03-18 10:34:00 | 53.542 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1642295 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-03-18 11:20:03 | 53.53983 N, 3.64233 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1624111 | Currents -subsurface Eulerian | 2011-03-18 11:25:00 | 53.53983 N, 3.64233 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1642326 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-03-18 11:40:00 | 53.5385 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1642338 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-03-18 11:40:00 | 53.5385 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1642351 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-03-18 11:40:00 | 53.5385 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1642246 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-03-18 11:40:01 | 53.5385 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1642271 | Hydrography time series at depth | 2011-03-18 11:40:01 | 53.5385 N, 3.64017 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1150124 | CTD or STD cast | 2011-03-18 11:55:00 | 53.54067 N, 3.64167 W | RV Prince Madog PD07/11 |
| 1117735 | CTD or STD cast | 2011-04-20 11:12:00 | 53.5395 N, 3.63167 W | RV Prince Madog PD11/11 |
| 1117747 | CTD or STD cast | 2011-04-20 12:05:00 | 53.53883 N, 3.63783 W | RV Prince Madog PD11/11 |
| 1118683 | CTD or STD cast | 2011-06-07 00:35:00 | 53.53917 N, 3.63383 W | RV Prince Madog PD43/11 |


